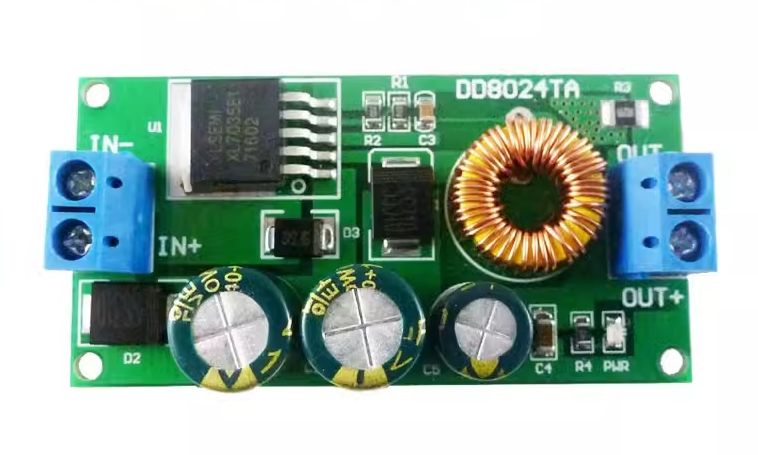
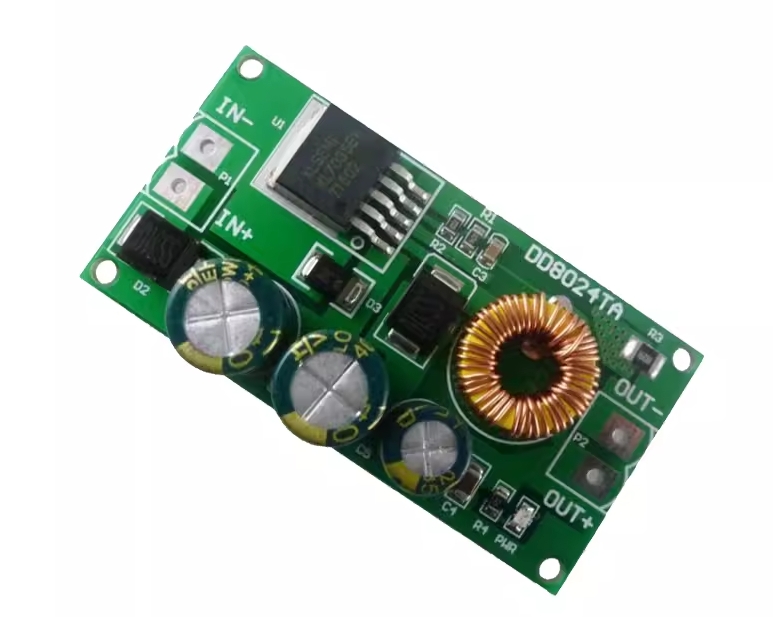
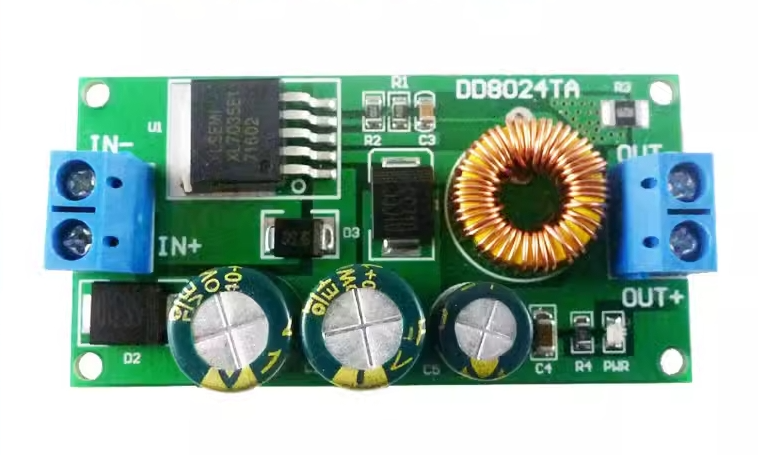
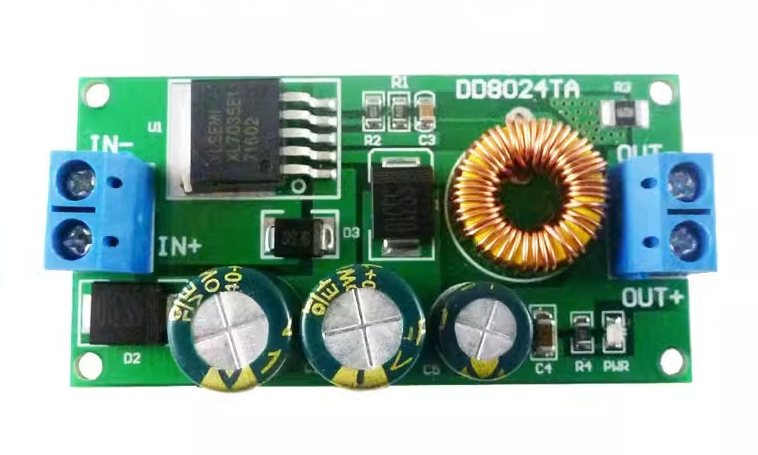
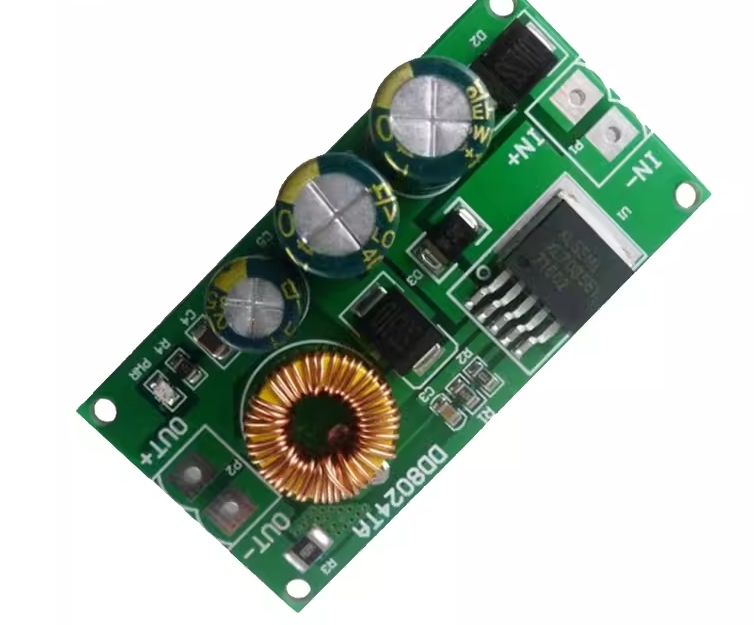
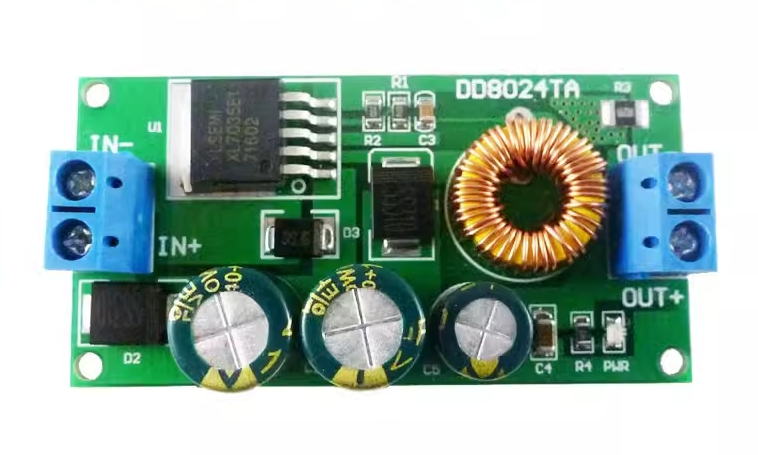
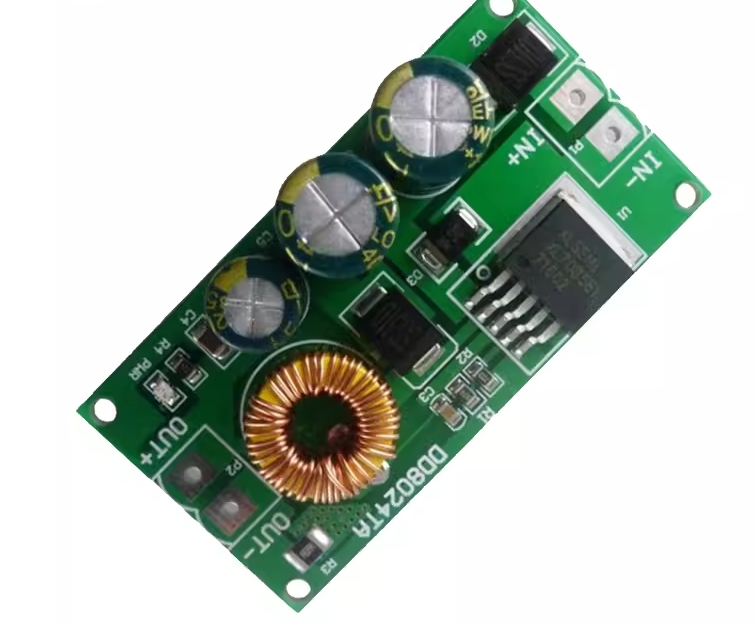
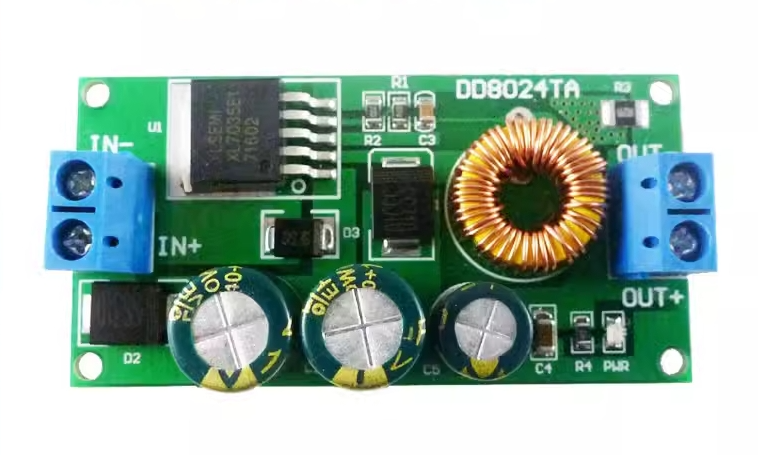
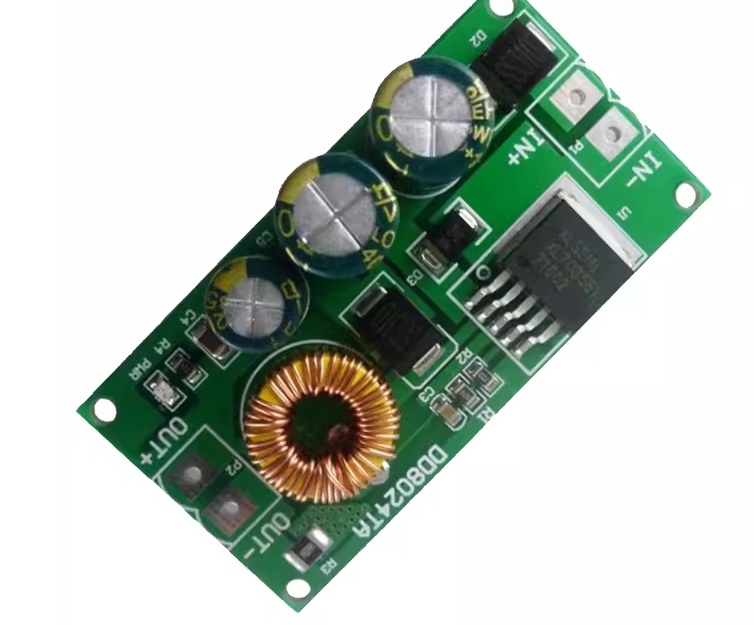
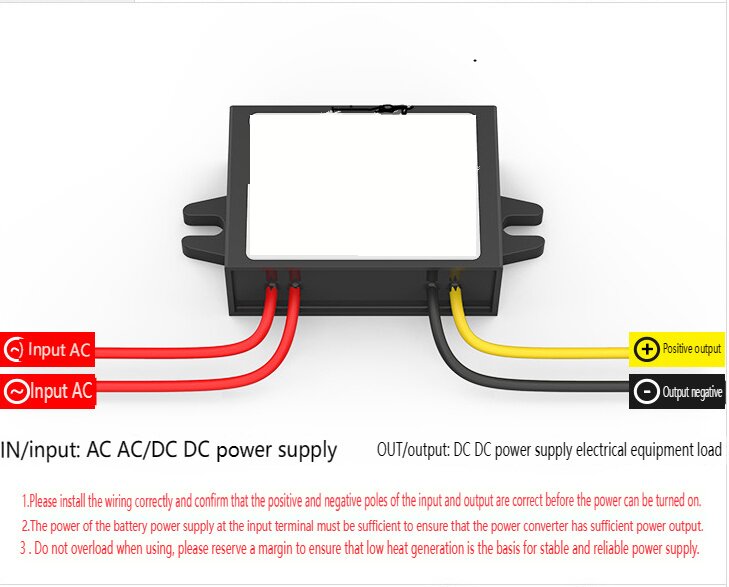
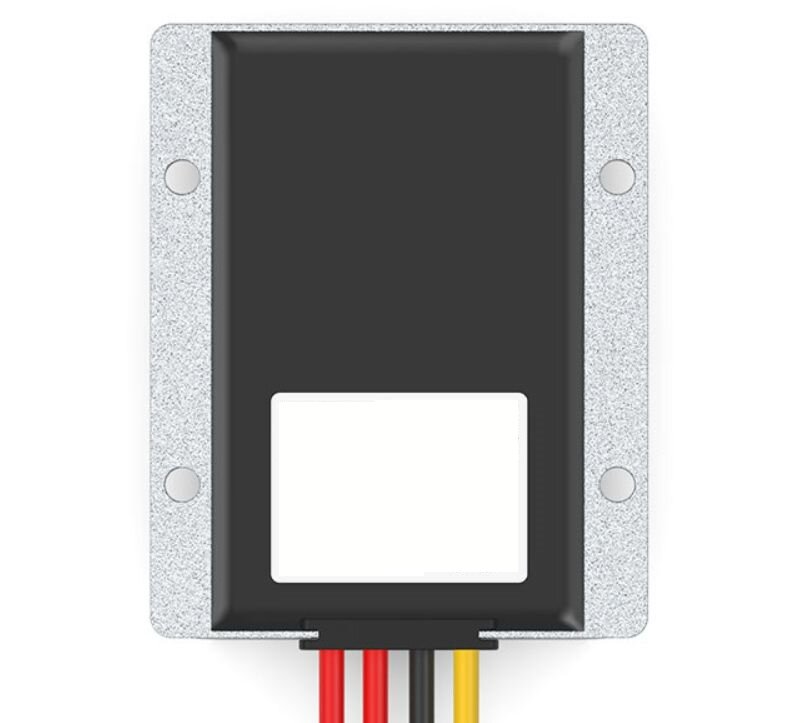
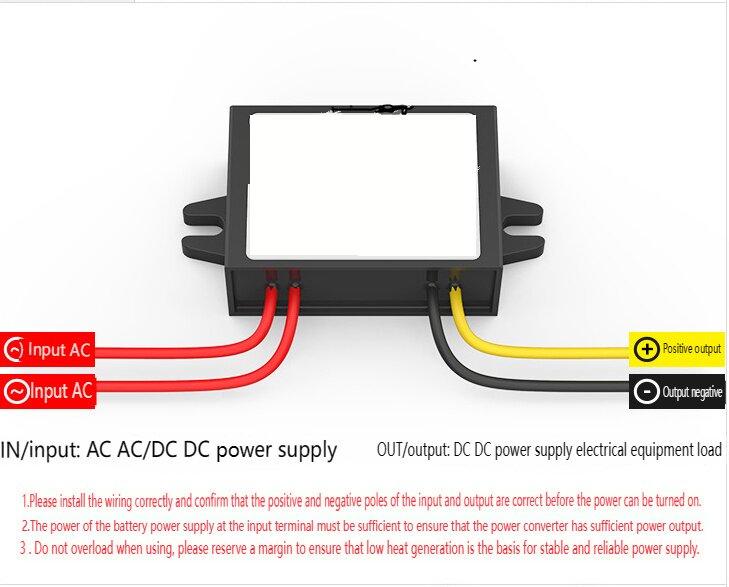
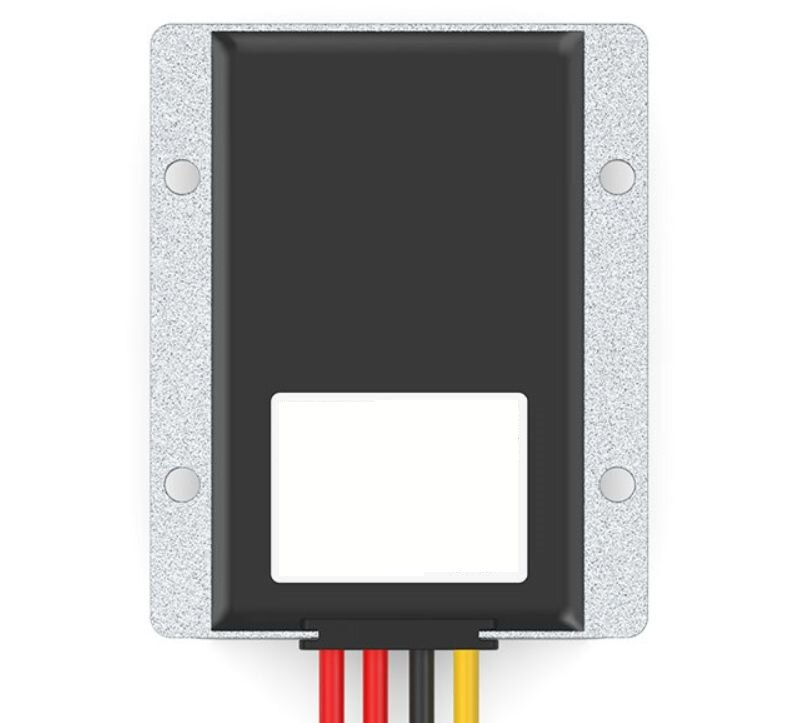
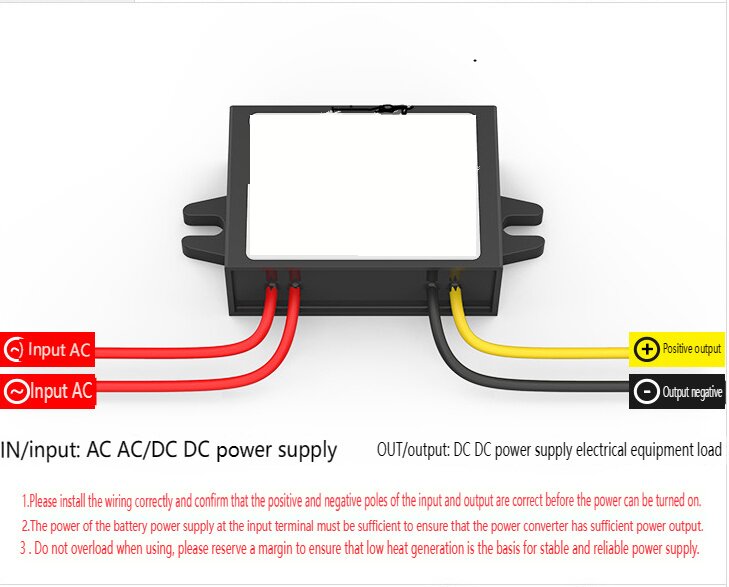
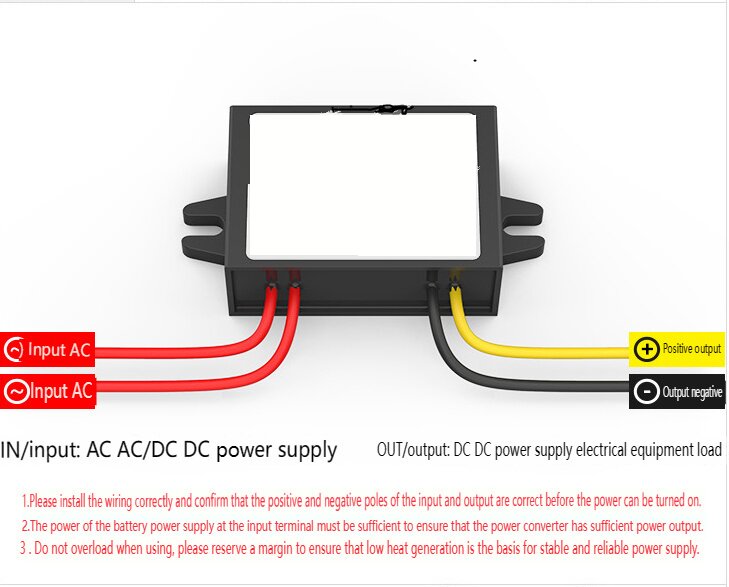
| AC to Dc buck stabilized power supply module |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZaxr | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| AC to Dc high-power switching power supply buck module |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | A device that can make a constant current form in the circuit, such as a dry battery, a storage battery, a DC generator, etc., is called a DC power supply. DC power supply has two electrodes, positive and negative, the potential of the positive electrode is high, and the potential of the negative electrode is low; When the two electrodes are connected to the circuit, the DC power supply can maintain a constant potential difference between the two electrodes, thus forming a constant current from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit. In order to keep the potential difference between the two poles of the DC power supply constant, the positive charge flowing from the positive electrode to the negative electrode in the external circuit must return from the negative electrode to the positive electrode in the direction of the electric field force in the power supply. This process cannot be achieved by electrostatic force, but only by some kind of "non-electrostatic force" that is opposite to the direction of the electrostatic force. The role of the AC-DC power module. Isolation: 1. Safety isolation: strong and weak current isolation, IGBT isolation drive, surge isolation protection, lightning isolation protection (such as isolation protection of medical electronic equipment in contact with the human body). 2. Noise isolation: (isolation of analog circuit and digital circuit, isolation of strong and weak signals). Grounding loop elimination: remote signal transmission distributed power supply system. Protection Short-circuit protection, over-voltage protection, under-voltage protection, over-current protection, and other protections. 3. Voltage conversion Boost Conversion Buck Conversion AC/DC Conversion (AC/DC, DC/AC) Polarity Conversion (Positive and Negative Polarity Conversion, Single Supply and Positive and Negative Supply Conversion, Single Supply and Multiple Supply Conversion) Fourth, voltage stabilization AC mains power supply, remote DC power supply, distributed power supply system, battery power supply. | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| AC 220V to Dc high-power transformer |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| AC to Dc transfomer buck module regulator |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | DGEB | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| AcDc linear power supply 220W to positive and negative voltage |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA, Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc PCB size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3 | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | Module type Linear power supply Ultra-low ripple Input voltage 220V(AC) Please pay attention to electrical safety Output voltage Multiple versions are available Taxi 5V, +9V, +12V, Earth 15V ± 200mA, 400mA, 600mA, +800mA. Output current Multiple versions are available taxi 1000mA Output ripple Better than 1mV Idle Positive pressure: 15.4pVRMS Module noise (10Hz to 100kHz) Negative pressure: 15.1 pVRMS Module PSRR 72dB (120Hz) Module enabled not Module protection. Output overcurrent protection The output comes with a resettable fuse Module features: multiple Low noise, low ripple; With power indicator Precision operational amplifier power supply, high-speed/high-precision data conversion module application multiple Power supply for switches, sensors, MCUs, etc Module weight 390g PCB. Size 122×52×39 Length×W×H(mm) The module heats up The greater the load, the greater the heat Operating temperature 0 ℃-70℃ Civilian grade Module interfaces Input: 8-character power socket; Output: XH2.54-3P*3. | KW-KEJI | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| DC transformers |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| DC-DC buck power board |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | diymore | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| DC-DC power supply buck module |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | SZQJXKJ | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | | | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |
| MW-High-power switching power supply |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| | High-Power Switching Power Supply Switching power supply design is a relatively new approach that solves many of the problems that exist in linear power supply design, including transformer size and voltage regulation. In a switching power supply design, the input voltage is no longer reduced, but rectified and filtered at the input, then converted into a high-frequency pulse train by a chopper, and filtered and rectified again before the voltage reaches the output. The switching transistor used in the switching power supply is mostly switched between the fully open mode (saturation zone) and the fully closed mode (cut-off zone), both modes have the characteristics of low dissipation, and the conversion between the switching will have a higher dissipation, but the time is very short, so it is more energy-saving and produces less waste heat. Ideally, the switching power supply itself does not consume electrical energy. Voltage regulation is achieved by adjusting the timing of transistor conduction and circuit breaking. Conversely, in the process of generating the output voltage of a linear power supply, the transistor operates in the amplification area, which itself consumes electrical energy. The high conversion efficiency of the switching power supply is one of its major advantages, and because the switching power supply works at a high frequency, a transformer with a small size and light weight can be used, so the switching power supply will be smaller than the linear power supply, and the weight will be relatively light. | MW-KG | In Stock | New Sealed Under Guarantee | | |
| |